Viewing Images¶
nuts-ml provides functions to show images on the fly. The following
example reads two images using ReadImage and then displays the loaded
images in column 0 of the samples via ViewImage:
>>> samples = [('nut_color.gif', 'color'), ('nut_monochrome.gif', 'mono')]
>>> imagepath = 'tests/data/img_formats/*'
>>> samples >> ReadImage(0, imagepath) >> ViewImage(0, pause=1) >> Consume()
The output is a viewer window that displays the images with a pause of 1 second:
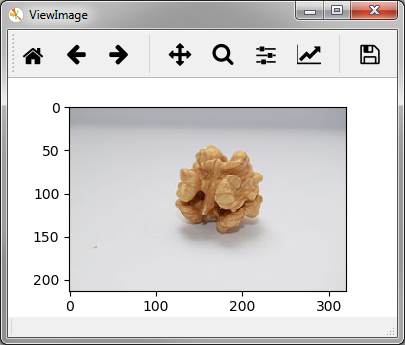
Sometimes samples contain multiple images. For instance, an input image and
an output mask for segmentation tasks. ViewImage allows to display the
multiple images of a sample at the same time by providing the column indices
(here 0 and 1) of the sample that contain the images:
>>> samples = [('color.jpg', 'monochrome.jpg'), ('color.png', 'monochrome.png')]
>>> imagepath = 'tests/data/img_formats/nut_*'
>>> samples >> ReadImage((0,1), imagepath) >> ViewImage((0,1), pause=1) >> Consume()
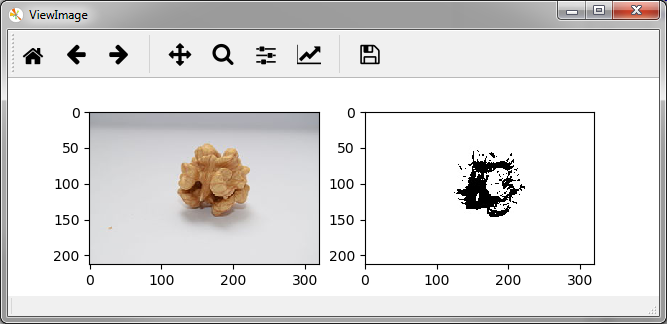
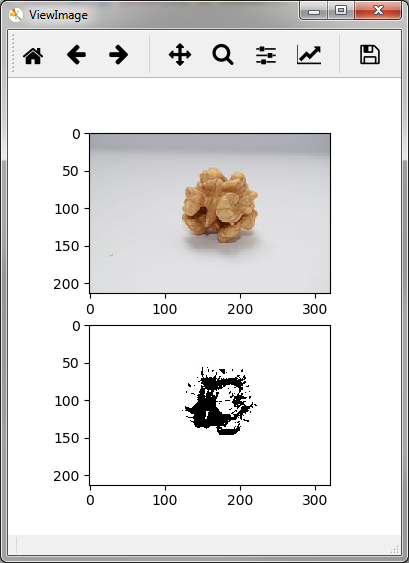
Per default multiple images are display in a single row. The parameter layout
allows to specify the rows and columns the images are arranged in,
e.g. a layout of (2,1) states that 2 images are to be arranged in 2 rows and 1 column:
>>> (samples >> Print() >> ReadImage((0,1), imagepath) >>
... ViewImage((0,1), layout=(2,1), pause=1) >> Consume())
('color.jpg', 'monochrome.jpg')
('color.png', 'monochrome.png')
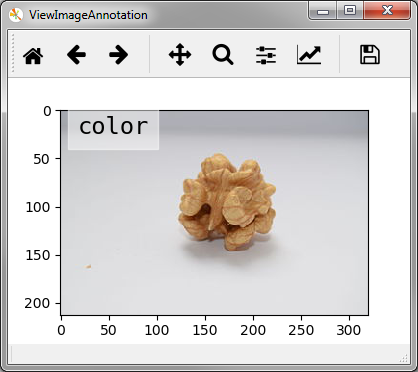
Often we want to show the class label in addition to the image and ViewImageAnnotation(imgcol, annocol) is designed for this purpose.
In addition to a column index for the image (imgcol) it also takes an index
for the sample column that contains the class label (here 1) and the
viewer displays the image with an overlay-ed text for the label:
>>> samples = [('nut_color', 'color'), ('nut_monochrome', 'mono')]
>>> imagepath = 'tests/data/img_formats/*.gif'
>>> samples >> ReadImage(0, imagepath) >> ViewImageAnnotation(0, 1, pause=1) >> Consume()
In the following sections we will introduce the functions for image transformation and augmentation.